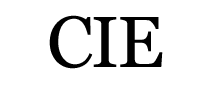Bayes Theorem
Summary Bayes theorem is basically defined as calculating the given probability when we know certain other probabilities. Bayes theorem can be written as: We have already studied conditional probability in the article ”Probability”. Let’s recall this before we move on to Bayes theorem. Conditional probability is when the probability of one event, given that the … Read more